Collagen is a crucial protein that is vital to the human body. It is the most abundant protein and provides structure and strength to various tissues, including the skin, bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. In this section, we will explore the different types of collagen found in the human body and their significance. We will also learn about the structure of collagen, how it is synthesized, and how it breaks down over time. Understanding the various types of collagen, their functions, and their roles in collagen synthesis and breakdown is essential to maintaining healthy skin, joints, and overall well-being. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of collagen!
As we delve further into explaining the different types of collagen in the human body, we need to understand why collagen is essential. Collagen is a protein that forms the connective tissue in your body. It is one of the primary components of skin, hair, nails, bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.
The human body has many different types of collagen, including Type I, Type II, Type III, Type IV, and Type V collagen. Each type has a unique structure and serves specific purposes in the body. We will discuss each type in detail and understand where they are found and their functions.
Now that you know the importance of collagen protein, let’s explore the collagen structure, synthesis, and breakdown in more depth.
Understanding Collagen: A Vital Protein
Collagen protein is a crucial building block for maintaining a healthy body. As the most abundant protein in our system, it provides structure and strength to various tissues such as the skin, bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. It is responsible for keeping our skin firm and elastic while also giving our joints the necessary cushioning to prevent injury.
Collagen comprises long amino acid chains that form a triple-helix structure. This unique structure helps strengthen various tissues and enables collagen to carry out its functions effectively. Additionally, collagen is also essential for wound healing, and it plays a crucial role in our body’s overall metabolism.
“Collagen is an absolutely vital protein for healthy skin, strong bones, and flexible joints. It is often referred to as the glue that binds our body together.”
The Different Types of Collagen
Collagen is a versatile protein of various types with unique functions and advantages.
| Type of Collagen | Location and Main Function |
|---|---|
| Type I collagen | Found in skin, bones, tendons, and connective tissue. Provides structure and support. |
| Type II collagen | Found in cartilage hyaline cartilage. Provides cartilage with shock-absorbing properties. |
| Type III collagen | Found in the skin, arteries, veins, and internal organs. Provides elasticity and strength to organs. |
| Type IV collagen | Found in the basement membrane. Supports cell adhesion and differentiation. |
| Type V collagen | Found in hair, placenta, and cell surfaces. Helps regulate cell growth and development. |
As you can see, each type of collagen has specific roles in the body and is present in different locations. Understanding the types of collagen and their function can help you choose the right collagen supplement or product for your needs.
Collagen Functions and Benefits
Collagen, being an essential protein, performs numerous functions and offers many benefits to our bodies.
- Structural support: Collagen provides structural support to various tissues such as bones, tendons, cartilage, and ligaments, which enables them to withstand tension and pressure.
- Skin elasticity: The dermis layer of the skin comprises collagen, which promotes elasticity and firmness, minimizing fine lines and wrinkles as we age.
- Joint health: Collagen improves our joints’ health and mobility by keeping cartilage healthy, preventing joint deterioration, and reducing joint pain and stiffness.
- Wound healing: Collagen aids in wound healing and tissue regeneration by attracting new cells to the site and providing a framework for new tissue growth.
- Heart health: Some studies suggest that consuming collagen peptides may help improve heart health by reducing cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
To reap the benefits of collagen, you can incorporate collagen supplements, bone broth, fish, and lean meat into your diet. However, before taking any supplements, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to avoid adverse effects.
“Collagen’s benefits go beyond skin-deep. It promotes healthy joints and reduces joint pain, strengthens bones, and boosts heart health. All of this makes collagen an essential protein for optimal overall health.”
Demystifying Collagen Structure
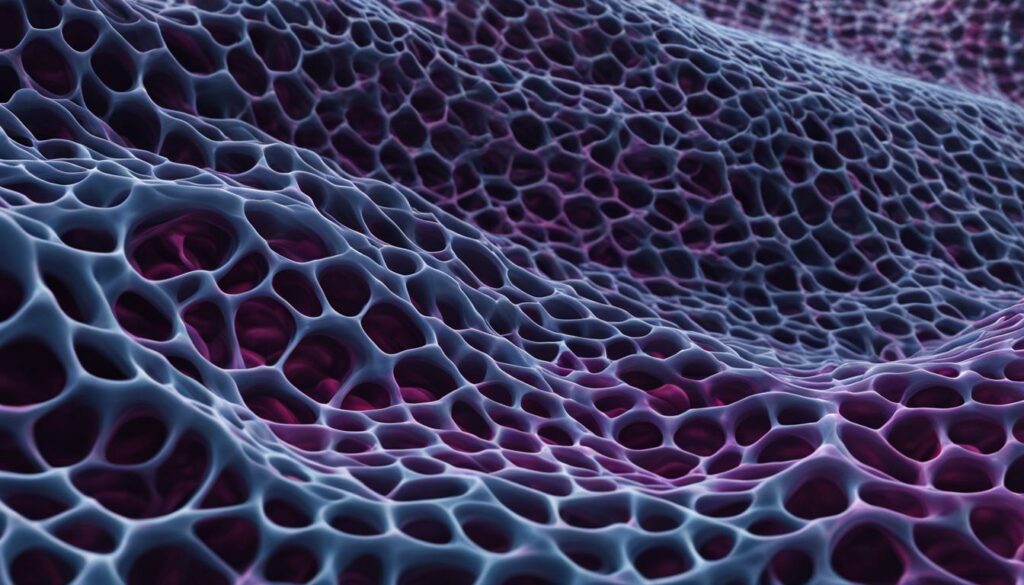
The structure of collagen is fascinating yet complex. Collagen is a fibrous protein comprising three chains of amino acids twisted together in a triple helix structure. This triple helix structure gives collagen unique strength and stability, making it the primary structural component of various tissues, including skin, bone, and cartilage.
The arrangement of collagen fibrils also plays a crucial role in defining the structural properties of collagen. Collagen fibrils are arranged in arrays, with each array having a specific orientation and length, creating a highly organized network of collagen fibers. Collagen cross-linking, a process that stabilizes collagen fibers, is crucial for maintaining the integrity and strength of collagen-rich tissues.
Studies suggest that collagen structure is affected by various factors, including age, disease, and environmental stressors. For instance, a decrease in collagen cross-linking can lead to changes in the shape and size of collagen fibrils, resulting in changes to the overall structure and function of collagen-rich tissues.
Overall, understanding the structure of collagen is vital to comprehend how it functions in the body and how we can protect and preserve it to maintain healthy skin, bones, and joints.
Collagen Synthesis: The Process of Production
Collagen synthesis is a complex process involving various steps, enzymes, and nutrients that must function harmoniously to create sufficient amounts of this critical protein. The process of collagen synthesis is initiated by fibroblasts, which generate the protein’s precursor, procollagen, translating the genetic code into amino acid chains. Afterward, specific enzymes modify and cleave the molecule, allowing it to form tropocollagen molecules. Furthermore, these molecules are assembled into fibrils and eventually cross-linked to create strong fibers, which give tissues their shape and structure.
Factors such as age, diet, stress, and environmental toxins impact normal collagen synthesis. In specific situations, certain conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan Syndrome, and other genetic disorders affect collagen production, leading to adverse health effects.
Eating a diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals, such as vitamin C, zinc, and copper, is essential to ensure adequate collagen production. Reducing exposure to stress and free radicals from environmental factors such as pollution can also help. Finally, regularly taking collagen supplements can also provide the body with the necessary materials to produce sufficient amounts of this critical protein.
Collagen Breakdown: Aging and External Factors
Collagen is a vital protein that gives structure and support to various body tissues. However, collagen breakdown accelerates as we age, leading to visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles and sagging skin. In addition to natural aging, several external factors can contribute to collagen breakdown, including:
- Sun exposure: UV rays damage collagen fibers, reducing collagen production and accelerating breakdown.
- Smoking: Smoking causes oxidative stress, reducing the body’s ability to produce collagen and breaking down existing collagen fibers.
- Poor diet: A diet lacking nutrients essential for collagen production, such as vitamin C and amino acids, can lead to decreased collagen synthesis and accelerated breakdown.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and incorporating collagen-supporting practices and products is essential to protect and preserve collagen. Wearing sunscreen, quitting smoking, and consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for collagen synthesis, such as vitamin C, are simple yet effective ways to slow collagen breakdown.
It’s never too late to take care of your collagen and keep your skin looking youthful and healthy!
Conclusion
In conclusion, collagen is an essential protein that plays a vital role in maintaining the structure and strength of various tissues in the human body, including the skin, bones, and cartilage. Understanding the different types of collagen, their functions, and their benefits can help us take proactive steps to protect and preserve collagen.
By incorporating collagen-supporting practices and products into our lifestyle, such as consuming collagen-rich foods, using collagen supplements, and protecting our skin from external factors contributing to collagen breakdown, we can maintain healthy skin, joints, and overall well-being.
While aging and external factors can accelerate collagen breakdown, it is never too late to start caring for our collagen health. With a little effort and the right mindset, we can promote optimal collagen production and enjoy its many benefits.

